Parsec splits the task of parsing a JSON API response and syncing it with Core Data into 3 steps:
- Validate the JSON against the JSON API spec. This ensures that the JSON we got from our API is compliant with the spec.
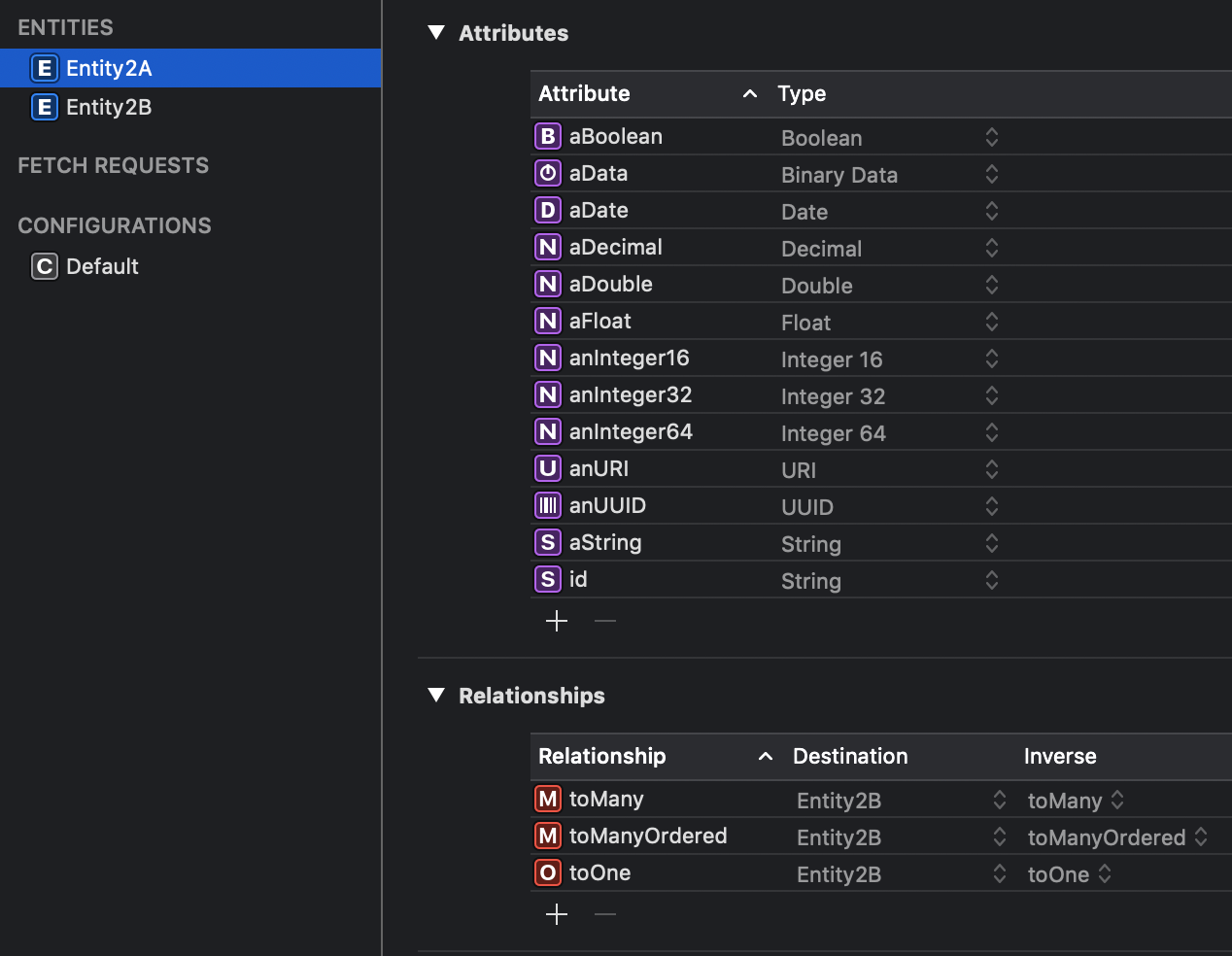
- Validate the JSON against the Core Data model. This ensures that all resources along with attributes and relationships can be mapped to our Core Data model correctly.
- Update a context with the parsed data in a single step.
{
"jsonapi":{
"version":"1.0"
},
"data":[
{
"id":"1",
"type":"entity2_a",
"attributes":{
"a_boolean":true,
"a_date":"2018-01-23T03:06:46Z",
"a_decimal":1.65,
"a_double":2.323,
"an_integer16":1,
"an_integer32":2,
"an_integer64":3,
"a_string":"lorem ipsum",
"an_uuid":"b8c01b3c-525a-4e33-ab02-6d8cdbd1e427",
"an_uri":"https://jsonapi.org"
},
"relationships":{
"to_one":{
"data":{
"id":"1",
"type":"entity2_b"
}
},
"to_many":{
"data":[
{
"id":"1",
"type":"entity2_b"
},
{
"id":"2",
"type":"entity2_b"
},
{
"id":"3",
"type":"entity2_b"
},
{
"id":"4",
"type":"entity2_b"
}
]
}
}
}
]
}let json: [String : Any] = …
let context: NSManageObjectContext = …
let parsec = Parsec()
do {
try parsec.update(context, with: json)
try context.save()
} catch {
}By default Parsec uses id (or remoteId) attributes from Core Data entities as the remote Id.
If you need to specify the remote Id for a particular entity, add parsec.isRemoteId and the value true to the attribute user info.
Parsec assumes your Core Data entities, attributes and relationships use camelCase notation. You can specify the naming convention used by your API using the .remoteNaming option. Valid options are:
snake_casehyphen
If no remote naming is specified, Parsec defaults to camelCase.
Example:
let json: [String : Any] = …
let context: NSManageObjectContext = …
let parsec = Parsec(parser: nil, options: [.remoteNaming : NamingConvention.hyphen])Parsec comes with a built-in Base 64 serializer for binary attributes and a ISO8601 serializer for date attributes. To specify a custom serializer for attribute, add parsec.serializer = mySerializer to the attribute user info.
Then, use the option key serializers to pass your custom serializers when creating a Parsec instance.
let serializers: [String : Serializer] = ["mySerializer" : MySerializer()]
let parsec = Parsec(parser: nil, options: [.serializers : serializers])If you don't want to import certain entity, attribute or relationship, you can prohibit importing by adding parsec.ignore = true in the user info of the excluded entity, attribute or relationship.
pod 'Parsec'