Warning: Experimental Feature
Manifold plugs into the Java compiler to enable you to use XML and Java seamlessly -- XML files are types. You use XML directly in Java type-safely without a code generator or extra build steps.
You can use XML, JSON, CSV, and YAML interchangeably, as such please refer to the JSON and JSON Schema project reference. All that applies to JSON applies to XML.
- Overview
- Naming
- Fluent API
- Creating & Building JSON
- Loading XML
- Request REST API services
- Writing XML
- Copying XML
- Using XML with JSON Schema
- IDE Support
- Setup
- Javadoc
- License
- Versioning
- Author
The XML type manifold provides comprehensive support for XML resource files (extension .xml). You can define an
XML API using a sample XML resource file. You can also define a JSON Schema version 4 or
later and use that as the schema for your XML files. Your XML resource files serve as the single source of truth
regarding XML APIs. You use XML-expressed types directly in your code without maintaining a separate set of classes
or wedging a code generator into your build.
Here is a sample XML file resources/com/example/Catelog.xml:
<ProductListing season="Fall">
<Store name="Valley #2">
<Address city="Cupertino" state="CA" postal="95014">
<Line order="1">1101 Broadway Dr</Line>
<Line order="2">Suite #123</Line>
</Address>
</Store>
<Product department="Men's" brand="Joe's" price="65.00"
description="Joe’s® 430™ Athletic Cut Jeans">
<Size waste="26-42" inseam="28-38" cut="Athletic"/>
</Product>
<Product department="Men's" brand="Squarepants" price="35.00"
description="Squarepants® Unround™ Pants">
<Size waste="25-49" inseam="25-36" cut="Athletic"/>
</Product>
<Product department="Jewelry" brand="RiteTwice" price="100.00"
description="RiteTwice® The 5 o'clock watch">
<Size wrist="XS-XL"/>
</Product>
</ProductListing>Most type manifolds, including the XML, JSON, CSV, & YAML manifolds, follow the Java naming convention where a type name is based on the
resource file name relative to its location in the resource path. Thus the XML resource file resources/com/example/Catelog.xml
has the Java type com.example.Catelog.
XML types are defined as a set of fluent interface APIs. For example, the Catelog XML type is an interface and
provides type-safe methods to:
- create a
Catelog - build a
Catelog - modify properties of a
Catelog - load a
Catelogfrom a string, a file, or a URL using HTTP GET - request Web service operations using HTTP GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, & DELETE
- write a
Catelogas formatted JSON, YAML, CSV, or XML - copy a
Catelog - cast to
Catelogfrom any structurally compatible type includingMaps, all without proxies
You create an instance of a XML type using either the create() method or the builder() method. Note if you want to
load data from preexisting XML files or even load directly from the sample data you can use the load() method or
the fromSource() method, discussed later in this document.
The create() method defines parameters matching the required properties defined in the JSON Schema, if the type is
plain XML or no required properties are specified, create() has no parameters.
Since Catelog is a plain XML file, as opposed to a JSON Schema structured XML file, you can create an empty
instance of Catelog with create() and then modify it using setter methods to change properties:
import com.example.Catelog;
...
Catelog catelog = Catelog.create();
catelog.setProductListing( makeProductListing() );Alternatively, you can use builder() to fluently build a new instance:
var listing = Catelog.ProductListing.builder()
.withSeason("Spring")
.withStore(Store.builder()
.withName("Valley #2")
.withAddress(Store.Address.builder()
.withCity("Cupertino")
.withState("CA")
.withPostal("95104")
.withLine(lines)
.build())
.build())
.withProduct(loadProducts())
.build();
catelog.setProductListing(listing);You can initialize several properties in a chain of with calls in the builder. This saves a bit of typing with
heavier APIs. After it is fully configured call the build() method to construct the type.
Note if using JSON Schema
withmethods also serve as a means to initialize values forreadOnlyproperties.
In addition to creating an object from scratch with create() and build() you can also load an instance from
a variety of existing sources using fromSource() and load().
You can load the contents of the file directly using fromSource().
// Load from the contents of the Catelog type's origin file
Catelog catelog = Catelog.fromSource();You can load a Catelog instance from a XML, JSON, CSV, or YAML String:
// From a JSON String
Catelog catelog = Catelog.load().fromJson("..."); Load from a file:
// From an XML file
Catelog catelog = Catelog.load().fromXmlFile("/path/to/WinterCatelog.xml");
// From an JSON file
Catelog catelog = Catelog.load().fromJsonFile("/path/to/SummerCatelog.json");Invoke a REST API to load a Catelog using HTTP GET:
// From HTTP GET
Catelog catelog = Catelog.load().fromJsonUrl("http://api.example.com/catelog/$catelogId");Use the request() static method to conveniently navigate an HTTP REST API with GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, & DELETE:
String id = "2019.fall";
Catelog catelog = Catelog.request("http://api.example.com/catelogs").getOne("/$id");The request() methods provides support for all basic REST API client usage:
Requester<Catelog> req = Catelog.request("http://api.example.com/catelogs");
// Get all Catelogs via HTTP GET
List<Catelog> catelogs = req.getMany();
// Add a Catelog with HTTP POST
Catelog catelog = Catelog.builder()
.withSeason("Spring")
.withStore(Store.builder()
. . .
req.postOne(catelog);
// Get a Catelog with HTTP GET
String id = catelog.getId();
catelog = req.getOne("/$id");
// Update a Catelog with HTTP PUT
catelog.getStore().setName("Valley #2");
req.putOne("/$id", catelog);
// Delete a Catelog with HTTP DELETE
req.delete("/$id");An instance of an XML API object can be written as formatted text with write():
toXml()- produces an XML formatted StringtoJson()- produces a JSON formatted StringtoYaml()- produces a YAML formatted StringtoCsv()- produces a CSV formatted String
The following example produces a JSON formatted string:
Catelog catelog = Catelog.builder()
.withSeason("Fall")
.withStore(Store.builder()
. . .
String json = catelog.write().toJson();
System.out.println(json);Output:
{
"ProductListing": {
"season": "Fall",
"Store": {
"name": "Valley #2",
"Address": {
"city": "Cupertino", "state": "CA", "postal": "95014",
"Line": [
{"order": "1", "textContent": "1101 Broadway Dr"},
{"order": "2", "textContent": "Suite #123"}
]
}
},
"Product": [
{
"department": "Men's", "brand": "Joe's", "price": "65.00",
"description": "Joe\u2019s\u00ae 430\u2122 Athletic Cut Jeans",
"Size": {"waste": "26-42", "inseam": "28-38", "cut": "Athletic"}
},
{
"department": "Men's", "brand": "Squarepants", "price": "35.00",
"description": "Squarepants\u00ae Unround\u2122 Pants",
"Size": {"waste": "25-49", "inseam": "25-36", "cut": "Athletic"}
},
{
"department": "Jewelry", "brand": "RiteTwice", "price": "100.00",
"description": "RiteTwice\u00ae The 5 o'clock watch",
"Size": {"wrist": "XS-XL"}
}
]
}
}Use the copy() method to make a deep copy of any XML API object:
Catelog catelog = . . .;
...
Catelog copy = catelog.copy();Alternatively, you can use the copier() static method for a richer set of features:
Catelog copy = Catelog.copier(catelog).withProductListing(. . .).copy();copier() is a lot like builder() but lets you start with an already built object you can modify. Also like
builder() it maintains the integrity of the schema's declared mutability -- you can't change
readOnly fields after the copy() method constructs the object.
You can use XML, JSON, CSV, and YAML interchangeably, via the universal JSON API. This means you can also use XML with any JSON Schema API. You can also define a JSON Schema API using XML. As such please refer to the JSON and JSON Schema project reference regarding API usage specific to JSON Schema. All that applies to JSON Schema applies to XML.
Manifold is fully supported in IntelliJ IDEA and Android Studio.
Get the Manifold plugin directly from within the IDE via:
Settings ➜ Plugins ➜ Marketplace ➜ search: Manifold
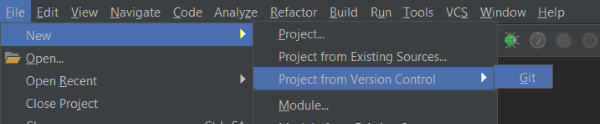
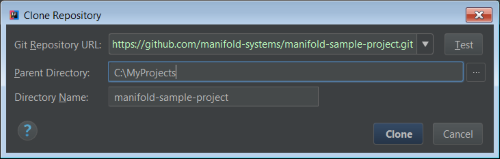
Experiment with the Manifold Sample Project via:
File ➜ New ➜ Project from Version Control ➜ Git
Enter: https://github.com/manifold-systems/manifold-sample-project.git
Use the plugin to really boost your productivity.
The manifold-xml project is defined with Maven. To build it install Maven and run the following command.
mvn compile
The manifold-xml dependency works with all build tooling, including Maven and Gradle. It also works with Java versions 8 - 21.
This project consists of two modules:
manifold-xmlmanifold-xml-rt
For optimal performance and to work with Android and other JVM languages it is recommended to:
- Add a dependency on
manifold-xml-rt(Gradle: "implementation", Maven: "compile") - Add
manifold-xmlto the annotationProcessor path (Gradle: "annotationProcessor", Maven: "annotationProcessorPaths")
If you are not using Maven or Gradle, you can download the latest binaries here.
Note, if you are targeting Android, please see the Android docs.
Note, if you are using Kotlin, please see the Kotlin docs.
Here is a sample build.gradle script. Change targetCompatibility and sourceCompatibility to your desired Java
version (8 - 21), the script takes care of the rest.
plugins {
id 'java'
}
group 'systems.manifold'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
targetCompatibility = 11
sourceCompatibility = 11
repositories {
jcenter()
maven { url 'https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/' }
}
dependencies {
implementation 'systems.manifold:manifold-xml-rt:2024.1.34'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
// Add manifold to -processorpath for javac
annotationProcessor 'systems.manifold:manifold-xml:2024.1.34'
testAnnotationProcessor 'systems.manifold:manifold-xml:2024.1.34'
}
if (JavaVersion.current() != JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8 &&
sourceSets.main.allJava.files.any {it.name == "module-info.java"}) {
tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {
// if you DO define a module-info.java file:
options.compilerArgs += ['-Xplugin:Manifold', '--module-path', it.classpath.asPath]
}
} else {
tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {
// If you DO NOT define a module-info.java file:
options.compilerArgs += ['-Xplugin:Manifold']
}
}Use with accompanying settings.gradle file:
rootProject.name = 'MyProject'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>my-xml-app</artifactId>
<version>0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>My Xml App</name>
<properties>
<!-- set latest manifold version here -->
<manifold.version>2024.1.34</manifold.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>systems.manifold</groupId>
<artifactId>manifold-xml-rt</artifactId>
<version>${manifold.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--Add the -Xplugin:Manifold argument for the javac compiler-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>11</source>
<target>11</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<compilerArgs>
<!-- Configure manifold plugin-->
<arg>-Xplugin:Manifold</arg>
</compilerArgs>
<!-- Add the processor path for the plugin -->
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>systems.manifold</groupId>
<artifactId>manifold-xml</artifactId>
<version>${manifold.version}</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Open source Manifold is free and licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
For the versions available, see the tags on this repository.